In this tutorial, going to discussed about the Jmeter, open source tool for performance testing.
Following are the topic we'll discussed in more details:
Performance Testing & Types of Performance testing
Pre Requisites
Jmeter Features
Jmeter installation
Jmeter Components
Test Plan and its elements
Creating a TestPlan
Thread Group
Sampler Controllers
Listeners and Timers
Logical Controller
Graphs and Reports
Performance Testing & Types of Performance testing:
Definition: Performance testing, in general, is testing performed to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular User load (concurrent users).
Other attributes Performance testing validates or verifies
Scalability
Reliability
Resource usage
Main Objective:
Find bottlenecks
Improve customer experience
Load testing: Evaluate the behavior of the application under increasing load. Identify the highest load the application is designed to perform correctly.
Stress testing: Evaluate a system or component at or beyond the limits of anticipated or specified workloads, or with reduced availability of resources such as access to memory or servers. This test is an attempt to break the system by suppressing its resources.
Spike Testing: Spike testing is done by suddenly increasing the load generated by users by a very large amount and observing the behavior of the system.
Soak Testing: Soak testing also known as endurance testing, is usually done to determine if the system can sustain the continuous expected load. During soak tests memory utilization is monitored to detect potential leaks.
Volume Testing: Testing whether the system is subject to large volumes of data.
Pre Requisites
Non Functional Requirements Document should be available which gives the details of the types of load test to be performed, number of concurrent users to be loaded, expected response time and other performance attributes to be captured.
Dedicated performance test environment to be available.
Test Environment should be like the actual production environment.
Get the details like the app server, DB server configurations etc.
Performance Test approach document should be ready and is signed off by all the concerned stake holders.
It’s free. It’s open source
It is 100% Java application
It has simple and intuitive GUI
It can do load and performance test on several servers:
Web - HTTP,HTTPS, SOAP
Database via JDBC, LDAP, JMS
Mail - POP3
It is platform-independent tool. On Linux/Unix, JMeter can be invoked by clicking on JMeter shell script jmeter.sh. On Windows it can be invoked by starting the jmeter.bat file.
JMeter store its test plans in XML format. This means you can generate a test plan using a text editor.
It is full multi-threading framework allows concurrent sampling by many threads and simultaneous sampling of different functions by separate thread groups.
It is highly extensible.
Controllers are configurable and can monitor server performance.
Test results can be captured in various format like summary report, aggregate report, graph, aggregate graph, results in tree, results in table
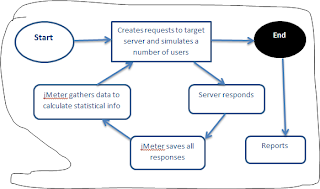
Jmeter life cycle
jmeter simulates a group of users sending requests to a target server, and return statistics that show the performance/functionality of the target server/application via tables, graphs etc.
 |
| Jmeter |
Jmeter Performance tool and installation
jMeter is an open source, pure Java application, software testing tool for load and performance testing
Installation:
Step 1: Install Java – JDK above version 6
If already installed, verify the version
Windows – Open Command Prompt - java -version
Linux – Open Command Terminal - $java -version
Step 2: Download jMeter: https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi
Step 3: Unzip the files to the destination folder
Step 4: Double click on jMeter.bat to open the application.
It will there in \apache-jmeter-2.11\bin\jMeter.bat
jMeter is an open source, pure Java application, software testing tool for load and performance testing
Installation:
Step 1: Install Java – JDK above version 6
If already installed, verify the version
Windows – Open Command Prompt - java -version
Linux – Open Command Terminal - $java -version
Step 2: Download jMeter: https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi
Step 3: Unzip the files to the destination folder
Step 4: Double click on jMeter.bat to open the application.
It will there in \apache-jmeter-2.11\bin\jMeter.bat
Fundamental jMeter Components
Test Plan: defines a series of steps on how and what to test. Only one test plan can be added per script and can be saved for future use.
Thread Group: Represents a set of actions added under test plan and can simulate multiple users.
Http request sampler: Records requests to web server and receives response
Elements of a Test Plan
A test plan provides a layout of how and what to test
Some of the test plan elements are:
Thread Group
Controllers
Listeners
Timers
Assertions
Configuration Elements
Pre-Processor Elements
Post-Processor Elements
Creating a test plan
Add the following elements to the test plan for a basic test scenario
Add number of users using Thread Group
Add default HTTP request from Config element
Add HTTP Request from Samplers
Add Listener to view results
Thread group
The thread group elements control the number of threads JMeter will use during the test.
To create the Thread Group, first run JMeter, from opened interface of JMeter choose Test Plan from the tree and right click to choose Add -> Threads (Users) ->Thread Group.
After opening thread Group, enter Thread Properties as given below
Number of Threads: The required number of Virtual users is specified here.
Loop Count: How many times (iterations) it is required to execute
Ramp-Up Period: How the load to be increased
Right click on the Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > Thread Group
Test Plan: defines a series of steps on how and what to test. Only one test plan can be added per script and can be saved for future use.
Thread Group: Represents a set of actions added under test plan and can simulate multiple users.
Http request sampler: Records requests to web server and receives response
Elements of a Test Plan
A test plan provides a layout of how and what to test
Some of the test plan elements are:
Thread Group
Controllers
Listeners
Timers
Assertions
Configuration Elements
Pre-Processor Elements
Post-Processor Elements
Creating a test plan
Add the following elements to the test plan for a basic test scenario
Add number of users using Thread Group
Add default HTTP request from Config element
Add HTTP Request from Samplers
Add Listener to view results
Thread group
The thread group elements control the number of threads JMeter will use during the test.
To create the Thread Group, first run JMeter, from opened interface of JMeter choose Test Plan from the tree and right click to choose Add -> Threads (Users) ->Thread Group.
After opening thread Group, enter Thread Properties as given below
Number of Threads: The required number of Virtual users is specified here.
Loop Count: How many times (iterations) it is required to execute
Ramp-Up Period: How the load to be increased
Right click on the Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > Thread Group
Change the name of My Thread Group, we can put as much as we want to put for load for concurrent user, loop count and all.
Right click on the My Thread Group > Add > Sampler > HTTP Request
Enter the Server or IP address
Listeners and Timers
Constant Timer
Constant Throughput Timer
Uniform Random Timer
Gaussian Random Timer
BeanShell Timer
Poisson Random Timer
BSF Timer
JSR223 Timer
Synchronizing Timer
Logical Controller
Logical Controllers: Logic Controllers let you control order of processing of Samplers in a Thread. Logic Controllers can change the order of request coming from any of their child elements.
Some examples are: For Each Controller, While Controller, Loop Controller, IF Controller, Run Time Controller, Interleave Controller, Throughput Controller, and Run Once Controller.
Listeners: Listeners are used to view the results in the form of graph, tree or numbers. Listeners like view results tree shows data for each item with details like request, response and transaction status and Summary report listener will give complete performance information, simulated users and details in numbers for each user.
Timers: Timers allow JMeter to delay between each request which a thread makes. Timer can solve the server overload problem.
Types of TimersConstant Timer
Constant Throughput Timer
Uniform Random Timer
Gaussian Random Timer
BeanShell Timer
Poisson Random Timer
BSF Timer
JSR223 Timer
Synchronizing Timer
Logical Controller
Logical Controllers: Logic Controllers let you control order of processing of Samplers in a Thread. Logic Controllers can change the order of request coming from any of their child elements.
Some examples are: For Each Controller, While Controller, Loop Controller, IF Controller, Run Time Controller, Interleave Controller, Throughput Controller, and Run Once Controller.
Results & Listener
Right click on the My Thread Group > Add > Listener > Select any one of listener.
Right click on the My Thread Group > Add > Listener > Select any one of listener.
Save it and click My Thread Group > Start button on menu button or Run > Start.
Best Practices: Do/Don't
Do not use GUI mode: Run Jmeter in non gui mode. Use jmeter –n-t test.jmx test.jtl
Use Remote and Distributed testing for larger load testing
Do not load more than 300 threads (Vusers) per plan
Do not add listeners & graphs to the Jmeter test plan. Write the results to a file in the system
Erase the local path of all the CSV data set config files
Use naming conventions for all the elements
Do not use XPATH extractor
Generate reports after run
Only save the data that is needed
Do not use assertions unless required.
Do not use GUI mode: Run Jmeter in non gui mode. Use jmeter –n-t test.jmx test.jtl
Use Remote and Distributed testing for larger load testing
Do not load more than 300 threads (Vusers) per plan
Do not add listeners & graphs to the Jmeter test plan. Write the results to a file in the system
Erase the local path of all the CSV data set config files
Use naming conventions for all the elements
Do not use XPATH extractor
Generate reports after run
Only save the data that is needed
Do not use assertions unless required.
If you like your self, you will like other as well!








Nice post By reading your blog, i get inspired and this provides some useful information. Thank you for posting this exclusive post for our vision.
ReplyDeleteDigital Marketing Training India